- Home
- Blogs
- Design Guides & Tips
- Led Lights & Ceiling Fans Buying Guide
LED Lights & Ceiling Fans Buying Guide
Tags: Light Bulbs
By: Shades of Light
Date: 2017-03-13
-
• Incandescent: When we think of a light bulb, odds are, the picture that pops into our heads is of a traditional incandescent bulb. Incandescent lamps have a filament surrounded by a glass bulb filled with an inert gas which protects the filament from exposure to air and oxidation. They generate light by passing a current through a thin wire filament, which heats it until it glows.
-
• Halogen: Halogen lights are a type of incandescent bulb, but a much more specialized one. Halogen bulbs are made of a tungsten filament surrounded by a halogen gas. These specific materials combine to create a cyclical chemical reaction inside the bulb that generates light without the rapid degradation of the filament that causes normal incandescent bulbs to burn out so quickly. Halogen bulbs last longer than normal incandescent lights, are smaller, and generally shed brighter, cooler light. However, they operate at very high temperatures, meaning they require closer attention to safety and energy considerations.
-
• Fluorescent: Fluorescent lamps consist of a glass tube with a special coating on the inside that is filled with a combination of mercury vapor and another gas like neon or xenon. An electrical current is passed through the gas, causing the mercury to interact with the coating inside the tube which then produces light. To properly regulate the electrical current, fluorescent bulbs require a ballast, making them more costly to produce than incandescent bulbs. They are, however, much more energy efficient and produce higher light output— or lumens— at lower wattages than incandescent bulbs. Because they contain mercury, they may be considered a hazardous material with specific requirements for disposal when they are no longer in use.
-
• CFL: Compact Fluorescent Lamps, commonly called CFL bulbs, are fluorescent bulbs designed to be smaller— more compact— than typical fluorescent bulbs. The glass tube is often spiral-shaped, and they are ‘self-ballasted’-- a ballast built into the bulb itself (rather than the fixture) helps regulate the electrical current.
-
• Incandescent vs. Fluorescent: Incandescent bulbs are cheaper up front than fluorescent bulbs or CFLs, but have a lower lumen output and require more energy— higher wattages— to operate. Incandescent bulbs also have a shorter lifespan than fluorescent bulbs.
-
• Halogen vs. Incandescent: Halogen bulbs last longer, and generally have higher lumen output than standard incandescent bulbs, but they require very high heat to operate, which creates safety concerns and energy consumption concerns. (Halogen bulbs can also be quite delicate; unless the bulb is surrounded by an extra layer of protective glass, always wear gloves upon installation because the oils from our fingers can damage halogen bulbs and cause them to burn out more quickly.)
-
• CFL vs. LED: CFL bulbs are more efficient than incandescent bulbs, with lower wattages able to achieve higher lumens. This energy efficiency is even greater in LED bulbs. LED bulbs also offer a higher range of color temperature options and generally have a longer lifespan.
-
• Incandescent vs LEDs: Compared to LEDs, incandescent lights are physically hotter, offer little in the way of light color options, have a shorter life span, and use more energy to work. Generally speaking, LED bulbs can (and should!) replace incandescent bulbs in most household applications. Some exceptions include any application that requires the heat generated by incandescent bulbs— like lava lamps! Dimmable function may also make incandescent bulbs more attractive in very specific situations. All incandescent bulbs are dimmable. Conversely, only some LED bulbs have dimmable function. If you are replacing an incandescent bulb in a fixture with a dimmer, be sure that the LED you choose is capable of being dimmed. Non-dimmable LED bulbs placed in a dimmable fixture will have an unpleasant flicker when not operated at full power and will not pass through the typical range of color and lumen output that a dimmable LED will.
If you’ve shopped for a light bulb recently, you’re probably aware that LED light bulbs are pushing those tired incandescent and unsightly CFL bulbs to the sidelines. LED technology represents an increasingly popular type of lighting that centers both attractive design and efficiency, so you don’t have to sacrifice style for eco-friendly— and budget-friendly— illumination.
Though we consider LED bulbs to be relatively new compared to incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, LEDs (or light emitting diodes) have been around for decades. That little red light that flashes when you point your remote control at your TV? That’s an LED! LEDs work by passing a current through a small diode, which then emits photons — particles of light. While incandescent and fluorescent lights require larger bulbs to produce higher light output, LEDs have no size limitations, meaning they can pack a lot of illumination into an incredibly petite package. They are also longer lasting and use less energy than other light sources, making them the perfect choice for daily use.
Measuring Light: Lumens Vs. Wattage
To truly understand the benefits of LED lighting, we must first understand how light is actually measured. Most of us are familiar enough with incandescent lighting that we associate wattage with how much light a bulb produces. Wattage, however, is not actually a measure of light, but rather a measure of energy usage. The word lumen refers to how much light a bulb produces, and thus is a more accurate way to determine exactly what to expect from your bulb before you turn it on.
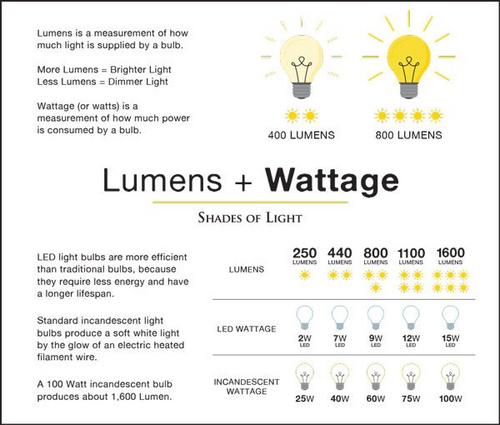
One of the major draws of LED lighting is that LEDs use less energy to achieve brighter light— in other words, LEDs use fewer watts to achieve the same or higher lumens as other types of bulbs. A typical 60-watt incandescent bulb produces about 800 lumens and a 60-watt halogen bulb produces about 900 lumens. Conversely, an 800 lumen CFL bulb may only use 13 watts, and an 800 lumen LED bulb uses as little 8 watts!
Tip: On Shadesoflight.com, when you view light bulbs, ceiling lights, and other light fixtures wattage and lumens measurements are provided in the product description.
Since we’re so used to thinking of a bulb’s brightness in terms of wattage, it can feel a bit strange or confusing to shop for more energy efficient bulbs. Some bulbs will list an ‘incandescent equivalent’ to help make the transition a little easier. It’s important to understand that high wattage is not required for bright light, and that the wattage requirements for your household fixtures are the maximum wattage that can be safely used in that fixture. You can always use a bulb that has a lower wattage than your fixture requires, but never a bulb with a higher wattage.
Practically speaking, this means if you make the switch to LED bulbs, you can often use brighter bulbs than the fixture can accept in traditional incandescent bulbs. If a fixture has a 60-watt max, you can only ever use a 60-watt incandescent bulb, amounting to about 800 lumens. But an LED bulb of 2500 lumens— equivalent to a 150-watt incandescent bulb— only uses about 22 watts, making it perfectly safe for use in the same fixture!aa
How Does Led Lighting Differ From Other Sources Of Light?
Since LED technology utilizes the most recent innovations in lighting tech, it’s natural to wonder how it compares to more traditional light sources. To get the most accurate picture of how LED lighting stacks up against other lights, let’s look at how other common lamps work!
So how do these various lighting technologies compare to each other and to LEDs?
If you’re unsure of the types of bulbs suitable for a specific fixture, always consult an electrician, as well as any safety labels and literature that come with that fixture.
Do Led Lights Raise An Electric Bill?
In short— not at all! LED bulbs are energy saving lights that are significantly more efficient than other types of bulbs. Not only do they use less energy day to day, but they also have a significantly longer lifespan than incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. Incandescent bulbs have a lifespan of around 2,000 hours— or a couple of months. Fluorescent bulbs have an average lifespan of around 30,000 hours, or a few years. While the lifespan of LED bulbs can vary, they average around 30,000 hours on the low end, and as much as 200,000 hours on the high end! That’s over twenty years of light from a single LED! Swapping out your incandescent bulbs and CFLs for LEDs is a great way to lower your energy consumption, reduce your electric bill, and dramatically simplify and reduce the inconvenience of dealing with a blown bulb. In the recent past, the upfront cost of LED bulbs has served as a deterrent to making the switch— LED bulbs are still a little more pricey than incandescent bulbs, but that difference in cost is shrinking pretty quickly, and the savings in the long run are substantial, making LEDs the all-around cheapest option for household light bulbs.
STAY IN THE KNOW
Be the first to find out about trending styles, new releases and sales.
#MyShadesofLight
Customer Service
B2B Programs
Our Company
Shopping Resources
© 2024 Shades of Light All Rights Reserved